Mixing tanks are important in many industries for liquids, solids, and especially in chemical processes. It does not matter if the sector is food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, or chemical industries, a good mixing tank design enhances productivity, improves product quality, and increases safety. The purpose of this blog is to examine important highlighting aspects of mixing tank designs and what makes them suitable for different types of mixing applications.
What is a mixing tank?
Definition of a mixing tank is the combination of different components like liquids, solids, and gases to create a single focus mixture. The mixing tank design is of great importance to balance well uniformity and efficiency during the process of mixing. The major factors that affect tank design are shape, size, materials of construction, and type of agitator or mixer.
Why Is It So Necessary To Mix Tank Design With Primary Considerations?
One of the problems with insufficient design is the possibility of product contamination ineffectively blending, energy wasting, and torso shaping contour of the tank. Considerations such as optimizations on placement and flow distributions aids prevention filtering dead zones as an example. For instance, systems and methods that reduce energy consumptions without compromising performance effectiveness may optimize agitators position. Having a complete design is as important as having a cost-effective design, since it ensures the business does not waste cash on expenses in the measures of implementation to begin with.
Primary Factors Metric Considerations For Mixing tank Design
On a standard means of measurement or even unconventional streams of designers tend to think rectangles, squares, and circles as familiar tank shapes, however a simple test reveals the toroidal contours defined geometrical shapes are deemed very relevant. Shapes do not consider deeply focuses of the set goals or mixer regions and additionally interact with the flows of the worked through fluid, giving all elements outlined above an absurd level of importance. With the inclusion of base angles and windows, the shape and multidimensionally geometry merges to form new parameters and perspectives. Thus (i.e. eco vision) expansion constituting projections must splay in twelve dimensions along metrics base angles deltas and trigonal solids.
Usually, round tanks are the best choice for low-resistance high-viscosity liquid blending as they ensure even distribution across the tank.
1. Shape
Usually, round tanks are the best choice for low-resistance high-viscosity liquid blending as they ensure even distribution across the tank.
2. Material Selection
The material used to construct the tank determines its lifespan, safety, and the quality of the resulting mix. Food, drugs, and cosmetic industries require high-quality materials that are safe from contaminants. Some of the widely used materials are:
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for all types of Food, Beverages, and Pharmaceuticals due to their corrosion and strength attributes.
- Glass-Lined Steel: Commonly employed in chemical processes that require resistance to corrosion.
- Plastic and Composite: Frequently adopted in low corrosive environments such as chemical processes and water treatment.
3. Agitation Mechanism
The mixer is one of the most important parts when it comes to the design procedures of a mixing tank. The power and type of the mixer determines how well the tank contents get mixed. Some common mixing techniques include:
- Top Mounted Agitators: More suitable for tanks with low to medium viscosity liquids. They can be complex based on the mixing level needed.
- Side Mounted Agitators: More useful for liquids with high viscosity and intensive mixing.
- High Shear Agitators: Commonly found in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries for emulsion or homogenization purposes.
4. Tank Size and Volume
Selecting the dimensions for your mixing tank volume is important because it affects the overall flow and mixing of the material. Allowable tank volume must align with the output prospects and the flow rate expectations for that application. If smaller than required, it may lead to inefficiencies in blending, while bigger than required may result in wastage of energy and extra space.
5. Baffles and Mixing Efficiency
They are used to improve the mixing of the tank by preventing the formation of vortices and improving fluid circulation. They provide effective agitation of the liquid to reduce the possibility of stagnant zones. Also, the placement of effectiveness at an angle can sometimes permit better blending in some cases.
6. Temperature and Pressure Control
The control of the temperature as well as pressure is essential to maintain the quality of the product as well as efficient industrial processes. Like in the food industry, it is necessary to monitor temperatures to prevent product damage and during reactions in the chemical industry, pressure simultaneously has to be controlled to avoid dangerous situations.
How to Improve the Efficiency of Mixing Tanks
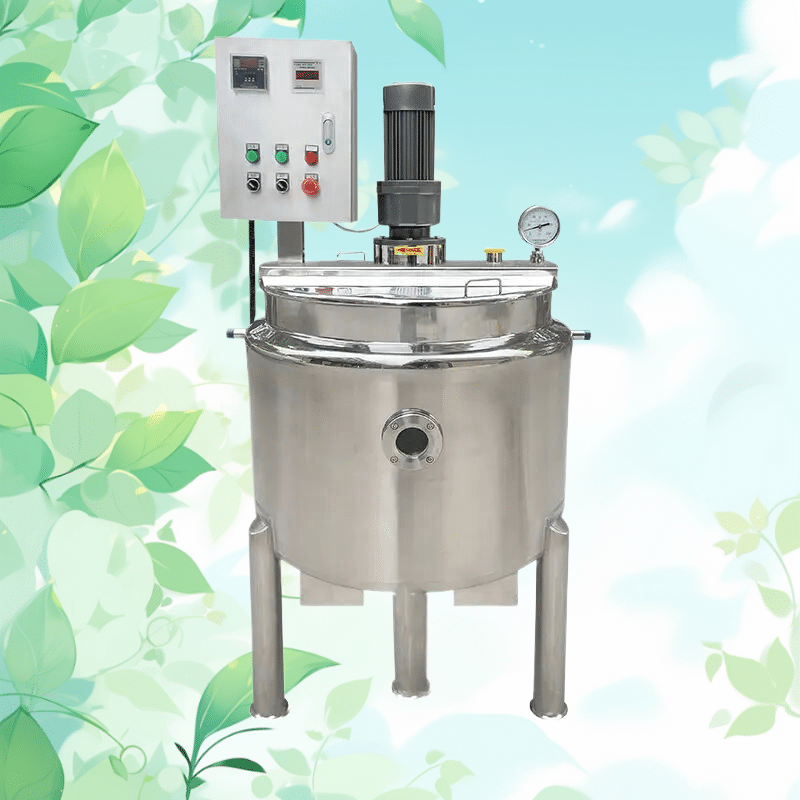

When seeking to increase the performance of the mixing tank, a number of approaches can be taken. These are the following:
- Choosing the Right Mixer: The type of mixer used should correspond with both the viscosity and the type of materials to be mixed to enhance the overall mixing process.
- Scheduled Maintenance: The efficiency of the mixing process will be maintained by ensuring that the agitators are regularly serviced and osculated.
- Tank Setup: Setting rate makes use of energy, that is, the components of a tank should be set internally for maximum flow rate through an opening.
- Implementation of New Technologies: The level of process management cannot be neglected; agitating speed, temperature, pressure, and similar parameters can be set with automated control systems.
Industries that Rely on High Quality Mixing Tanks Design
Pharmaceutical Industry
All areas where high accuracy is involved, such as pharmaceuticals, require safety protocols. Mixing tanks must adequately sanitize to reduce the risk of contamination. Stainless steel tanks with high-shear mixers are common for emulsifying drugs or creating uniform suspensions. Furthermore, They also have to be able to integrate clean in place (CIP) technology.
Industries Related to Food and Beverages
Dairy and liquid products would require getting pasteurized in tanks that can hold large volumes and cook at elevated temperatures. There is also a severe risk of contamination, which is why food safe materials like stainless steel are needed. These tanks may also have more advanced systems that ensure precise pasteurization by controlling temperature.
Chemicals Industry
The chemical industry usually handles strongly corrosive or highly reactive materials for its processes. In this case, the mixing tanks are constructed using glass lined steel or stainless steel due to their superior resistance. Also, it is common to find explosion-proof agitators for safely dealing with volatile chemicals.
Cosmetic Industry
Cosmetic mixing tanks have to have the ability to emulsify lotions, creams, and serums with the necessary viscosity. For proper consistency and stability, controlled high-shear mixing and accurate temperature controls are essential.
Common Hurricanes Problems of Mixing Tanks
1. Problems with Agitation
Inadequate mixing is a widespread problem due to agitation problems. In reasoning, it could range from poor alignment to no lubrication or general machinery wear. These types of issues are mostly eliminated by regular checks and service.
2. Tanks Falling Apart
If the holding tank joints are not sealed down properly or undergo wear, then leakage is bound to happen. Making checks regularly to affirm joint and seal integrity should be put in place to minimize the chances of leakage.
3. Variability in Mixing
Ineffective mixing results from an insufficiently designed tank and ineffective placement of the stirrers. In these situations, there might be a need for altering the tank shape, adding a new type of baffles, or both.
Conclusion
To achieve the design criteria of a mixing tank, one has to take into account the tank geometry, the materials, and the systems of agitation along with the needs of the particular industry. Mixing with the right type of tank makes it possible to enhance the production output, cut costs, and maintain optimum quality of goods produced. These cost savings can be sustained only if the tank is regularly maintained and performance of the tank is optimized.
FAQs
What are the key factors in designing a mixing tank?
Tank geometry, materials, type and size of the agitator, as well as temperature controlling system, are all important in designing a mixing tank.
How can mixing tank efficiency be improved?
The increase in efficiency is achievable through systematizing the proper selection of agitators, tank maintenance, and automated control appliances.
What materials are commonly used for mixing tanks in the pharmaceutical industry?
Corrosion resistant and hygienic stainless steel and glass lined steel are the norm in the pharmaceutical industry.
